Shuo Yu*, Hongyan Xue*, Xiang Ao, Feiyang Pan, Jia He, Dandan Tu and Qing He
Accepted by KDD 2023 Applied Data Science (ADS) track.
Abstract Link to heading
In the field of quantitative trading, it is common practice to transform raw historical stock data into indicative signals for the market trend. Such signals are called alpha factors. Alphas in formula forms are more interpretable and thus favored by practitioners concerned with risk. In practice, a set of formulaic alphas is often used together for better modeling precision, so we need to find synergistic formulaic alpha sets that work well together. However, most traditional alpha generators mine alphas one by one separately, overlooking the fact that the alphas would be combined later. In this paper, we propose a new alpha-mining framework that prioritizes mining a synergistic set of alphas, i.e., it directly uses the performance of the downstream combination model to optimize the alpha generator. Our framework also leverages the strong exploratory capabilities of reinforcement learning (RL) to better explore the vast search space of formulaic alphas. The contribution to the combination models’ performance is assigned to be the return used in the RL process, driving the alpha generator to find better alphas that improve upon the current set. Experimental evaluations on real-world stock market data demonstrate both the effectiveness and the efficiency of our framework for stock trend forecasting. The investment simulation results show that our framework is able to achieve higher returns compared to previous approaches.
Our Method Link to heading
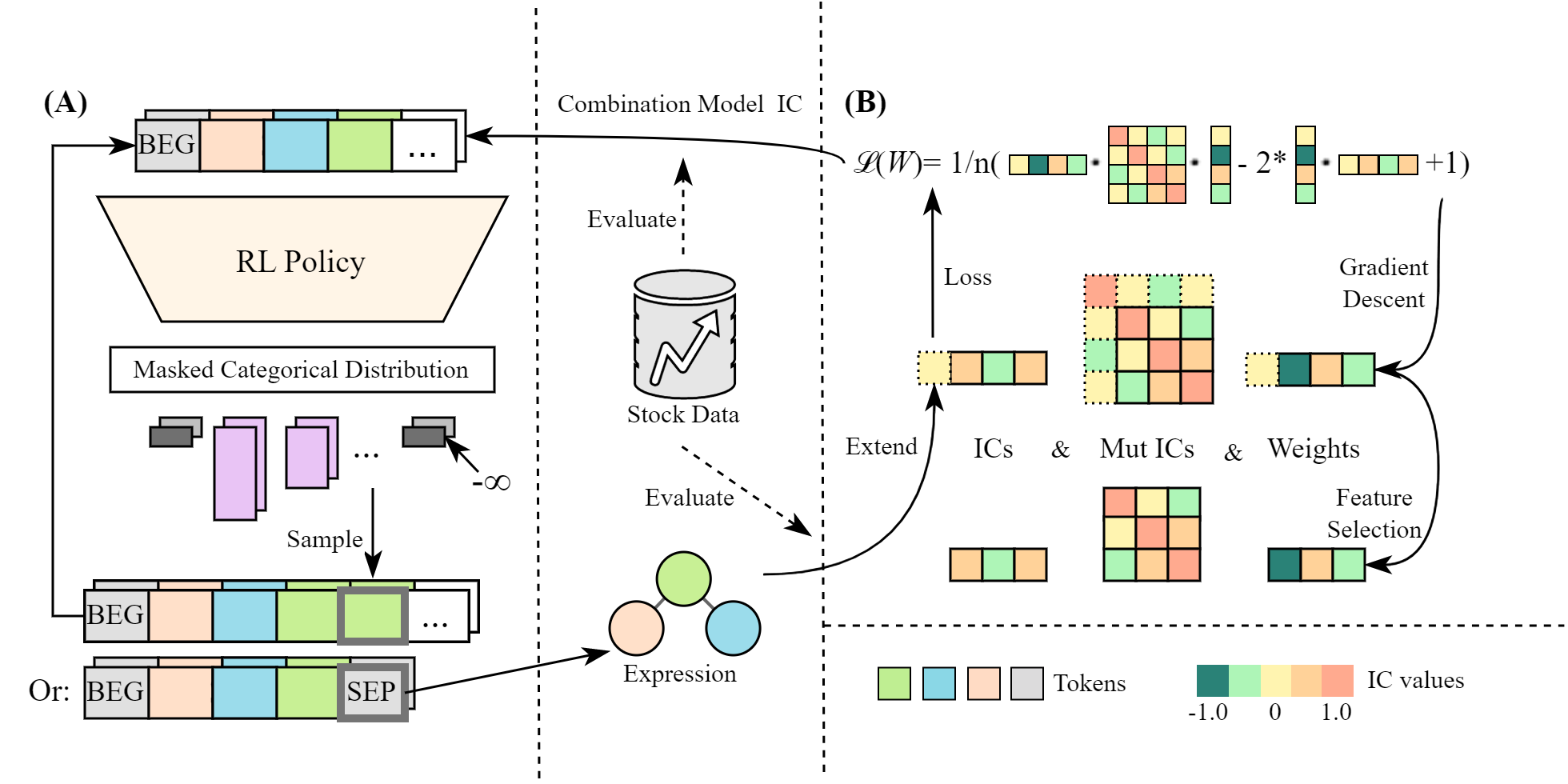
Our alpha-mining framework consists of two main components: 1) the Alpha Combination Model, which combines multiple formulaic alphas to achieve optimal performance in prediction, and 2) the RL-based Alpha Generator, which generates formulaic alphas in the form of a token sequence. The increment of performance in the Alpha Combination Model is used as the reward signal to train the RL policy in the Alpha Generator. Repeating this process, the generator is continuously trained to generate alphas that boost the combination model, thereby enhancing the overall predictive power.
The combination model consists of a set of alphas and their weights, and we consider the weighted linear combination of alphas as the overall pridictive signal. After the alpha generator outputs a new alpha, the alpha is first added to the candidate alpha set and assigned a random initial weight. Gradient descent is then performed to optimize the weights with respect to the extended alpha set. If the amount of alphas in the extended set exceeds a certain threshold, the least principal alpha is removed from the set together with its corresponding weight.
The alpha generator models a distribution of mathematical expressions. As each expression can be represented as a symbolic expression tree, we use the reverse Polish notation (RPN) to represent it as a linear sequence, since traditional auto-regressive generators can only deal with sequences. To control and evaluate the generation process of valid expressions, we model the generation process as a non-stationary Markov Decision Process (MDP): Each state corresponds to a sequence of tokens denoting the currently generated part of the expression, and an action is a token that follows the current state. The increment of performance in the Alpha Combination Model, and the dynamic is simply the sequence concatation. We choose PPO as the RL learner.
Our MDP has complicated rules for the legality of actions, including formal legality and semantic legality. We adopt the Invalid Action Masking mechanism to mask out invalid actions, ensuring formal legality; Invalid expressions receive the lowest rewards during run time, ensuring semantic legality.
Experimental results Link to heading
Our experiments are conducted on raw data from the Chinese A-shares market.
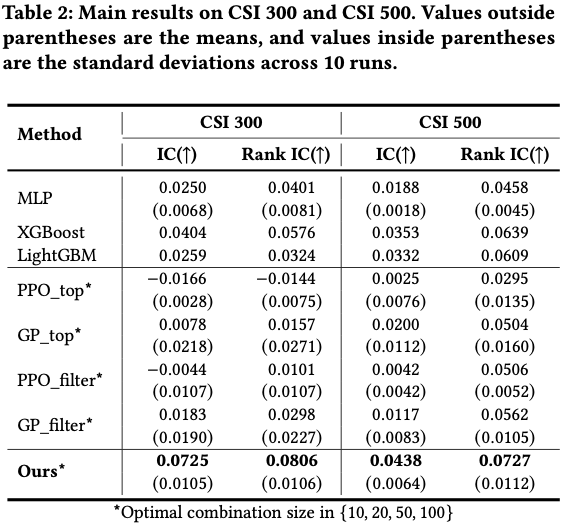
Compared with single-alpha oriented methods and some non-formulaic baselines, our framework is able to achieve the highest IC and rank IC, significantly outperformming baseline methods, and is also competitive against some commonly-used non-formulaic methods. Another case study also demonstrated that the combination IC is a better target than existing ones, including single-alpha IC and mutual IC between alphas.
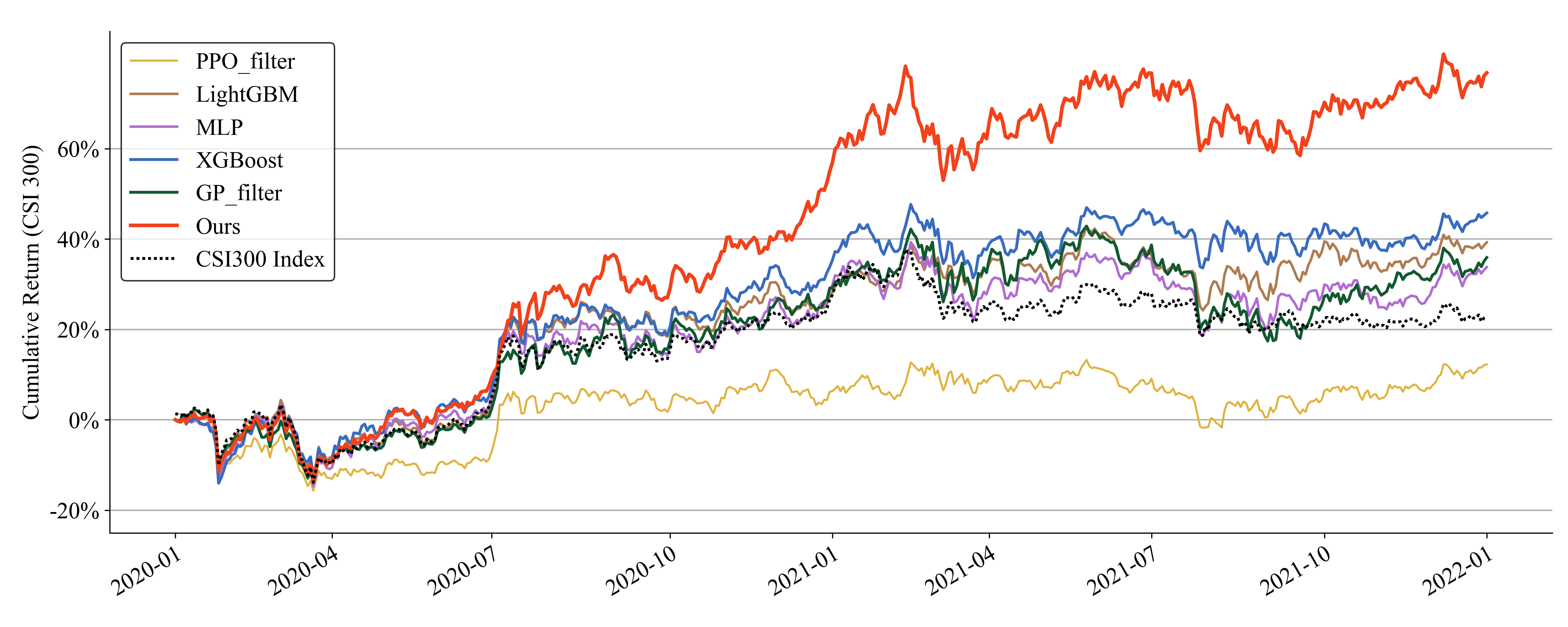
The investment simulation results show that our framework is able to achieve higher returns compared to previous approaches.